Karyomapping
Background
We handle the simpler case of a Trio with an affected child (ie proband/mother/father).
“In phase” implies that the allele from a parent is the same as that in the affected child
Variants are assigned to the following bins
F1ALT: Paternally inherited, in phase with affected child, ALT variant. F1REF: Paternally inherited, in phase with affected child, REF variant. F2ALT: Paternally inherited, out of phase with affected child, ALT variant. F2REF: Paternally inherited, out of phase with affected child, REF variant.
And vice versa for the mother. The only variants that fall into each of these situations are:
| Child GT | Father GT | Mother GT | Bin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/0 | F1ALT |
| 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | M1ALT |
| 0/1 | 0/1 | 1/1 | F1REF |
| 0/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | M1REF |
| 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | F2ALT |
| 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | M2ALT |
| 1/1 | 0/1 | 1/1 | F2REF |
| 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | M2REF |
Gene analysis
Menu: [analysis] -> [karyomapping]
Enter a gene name and click [Karyomap Gene] button.
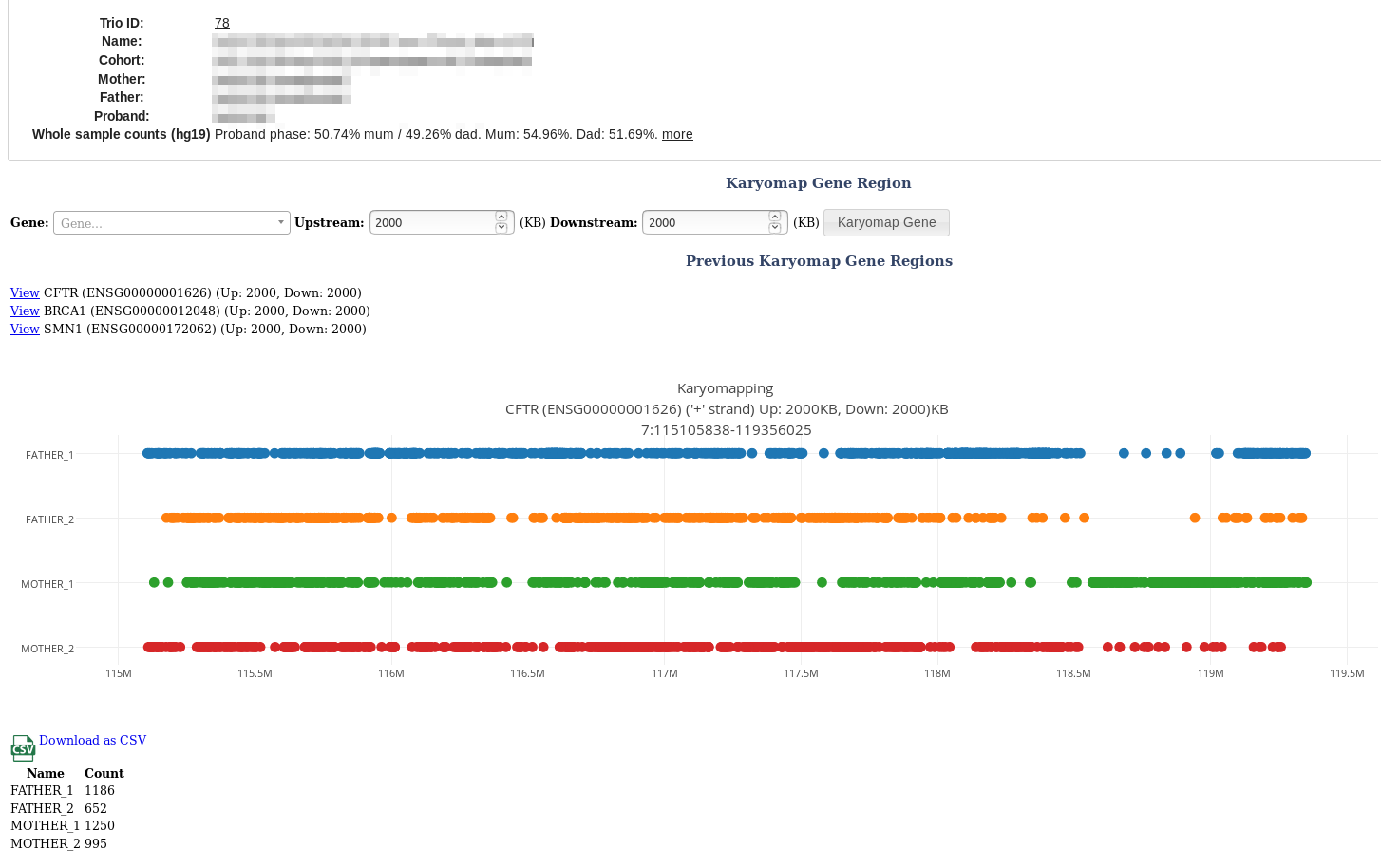
Genome-wide analysis
A genome wide karyomap count is performed when you create a trio. This is useful for finding sample mixups.
This is summarised as Proband phase: 50.74% mum / 49.26% dad. Mum: 54.96%. Dad: 51.69%. and is visible on the gene analysis screenshot above and the Trio page.
Proband phase shows the child’s marker percentage from each parent. Mum%/Dad% = Percent of parent markers that are in phase in proband.
Here are some examples for various Trios:
| Description | PP mum | PP dad | Mum % | Dad % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Trio 1 | 53% | 47% | 52.1% | 45.9 |
| Real Trio 2 | 52.3% | 47.7% | 46.1% | 45.9% |
| Bad Trio (Trio 1 with random dad) | 60.2% | 39.8% | 52.1% | 25.7% |
| Bad Trio (unrelated samples) | 48.5% | 51.6% | 30.8% | 29.8% |
| Bad Trio (mother/proband swapped) | 60.8% | 39.2% | 86.9% | 36.1% |
As a rough rule, you’d expect a minimum of 40% for an actual child.